The Tolerance settings define the minimum quality requirements that must be met when collecting points, lines, or polygons. They act as a quality filter, ensuring that recorded data meets predefined accuracy, reliability, and GNSS signal standards.
If the tolerances are not met, Locus GIS alerts the user that the limits have been exceeded. How to create and manages tolerances configuration, please see the article Manager of Tolerances
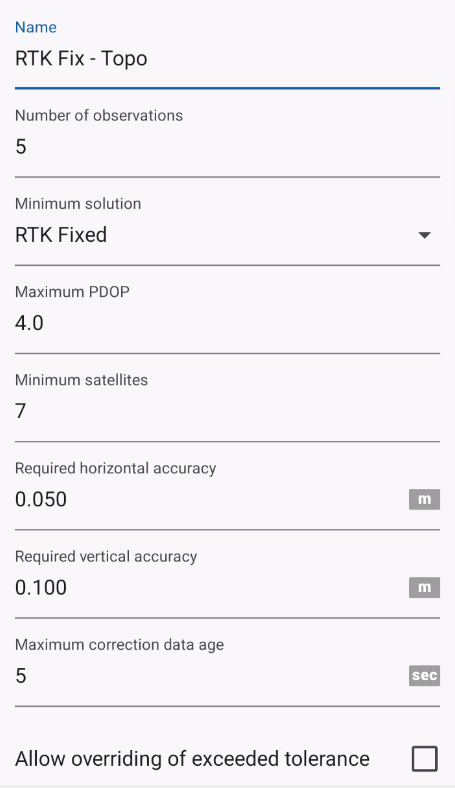
Tolerance Parameters
1. Name
A user-defined name for the tolerance profile (e.g. Default, RTK Survey, Mapping Grade). Allows you to create and reuse different tolerance profiles for different projects or accuracy requirements.
2. Minimum Solution
Defines the minimum GNSS positioning solution type that must be achieved.
Typical options may include:
- Autonomous (Standalone GPS)
- DGPS
- Float RTK
- Fixed RTK
Example of usage:
- Minimum solution = RTK Fixed → points will not be accepted unless RTK fix is achieved.
3. Maximum PDOP
Sets the maximum allowed Position Dilution of Precision (PDOP).
4. Minimum Satellites
Specifies the minimum number of GNSS satellites required to compute a position.
5. Required Horizontal Accuracy
Defines the maximum acceptable horizontal accuracy.
6. Required Vertical Accuracy
Defines the maximum acceptable vertical accuracy.
7. Maximum Correction Data Age
Specifies the maximum allowed age (in seconds) of GNSS correction data. It takes in account only if NTRIP is running
8. Allow Overriding of Exceeded Tolerance
Determines whether the user can manually accept data (save the data) that does not meet tolerance requirements.
Behavior of Empty Fields
If a tolerance field is left empty the parameter is ignored and no validation is applied for that parameter
